PTL: A
Model Transformation Language based on Logic
Programming
Jesus Almendros-Jimenez (1)
Luis Iribarne (2)
Jesus Lopez-Fernandez (3)
Angel Mora-Segura (3)
(1) Information System Group
jalmen@ual.es
http://www.ual.es/~jalmen
(2) Applied Computing Group
Luis.Iribarne@ual.es
http://www.ual.es/~liribarn
University of Almeria
04120 Almeria
SPAIN
(3) Autonomous University of Madrid
SPAIN
Abstract
In
this paper we present a model transformation language based on logic
programming. The language, called PTL (Prolog based Transformation
Language), can be considered as a hybrid language in which ATL (Atlas
Transformation Language)-style rules are combined with logic rules for
defining transformations. ATL-style rules are used to define mappings
from source models to target models while logic rules are used as
helpers. The implementation of PTL is based on the encoding of the
ATL-style rules by Prolog rules. Thus, PTL makes use of Prolog as a
transformation engine. We have provided a declarative semantics to PTL
and proved equivalent to the semantics of the encoded program. We have
studied an encoding of OCL (Object Constraint Language) with Prolog
goals in order to map ATL to PTL. Thus a subset of PTL can be
considered equivalent to a subset of ATL. The proposed language can be
also used for model validation, that is, for checking constraints on
models and transformations. We have equipped our language with
debugging and tracing capabilities which help developers to detect
programming errors in PTL rules. Additionally, we have developed an
Eclipse plugin allowing edition of PTL programs, as well as debugging,
tracing and validation. Finally, we have evaluated the language with
several transformation examples as well as tested the performance with
large models.
Contents
1. PTL interpreter, Debugger and Tracer
2. Examples of transformation
3. Instructions
4. Examples of models
5. Diagrams
6. Auxiliary
7. Eclipse plugin
8. Validation
1.- PTL interpreter, Debugger and Tracer
Source: ptl.pl
[home]
2.- Examples of transformation
a) EntityRelationship to Relational (PTL version): er2rl.ptl
b) EntityRelationship to Relational (ATL version): er2rl.atl
c) Examples taken from ATL ZOO: download ZIP version [ZIP]
d) Example of benchmarkings: [incquery.ptl]
[home]
3.- Instructions
a) Install SWI-Prolog from www.swi-prolog.org.
b) Start swi-prolog.
c) Load Prolog-based ATL interpreter:
?- [ptl]
d) Call
transformation example:
?- ptl('er2rl.ptl').
e)
Extras:
e.1) Debugging:
?-
debug('er2rl.ptl').
e.2)
Tracing:
?-
trace('er2rl.ptl',XMI_Id).
where
XMI_Id is
the XMI Id of some target element.
[home]
4.- Examples of models
XMI sources: model-A.xmi, model-B.xmi
[home]
5.- Diagrams
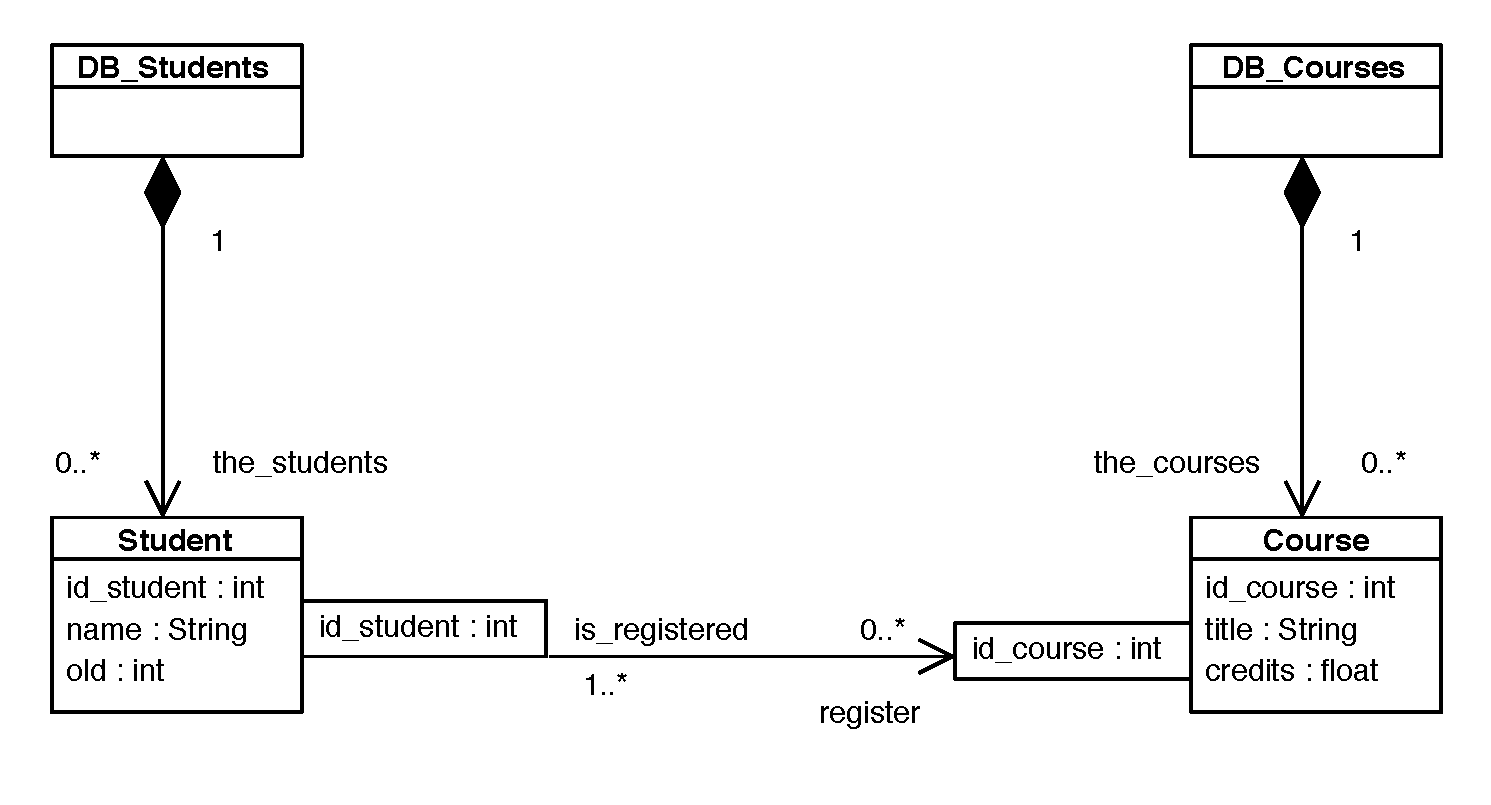
[home] [PNG]
[PDF]
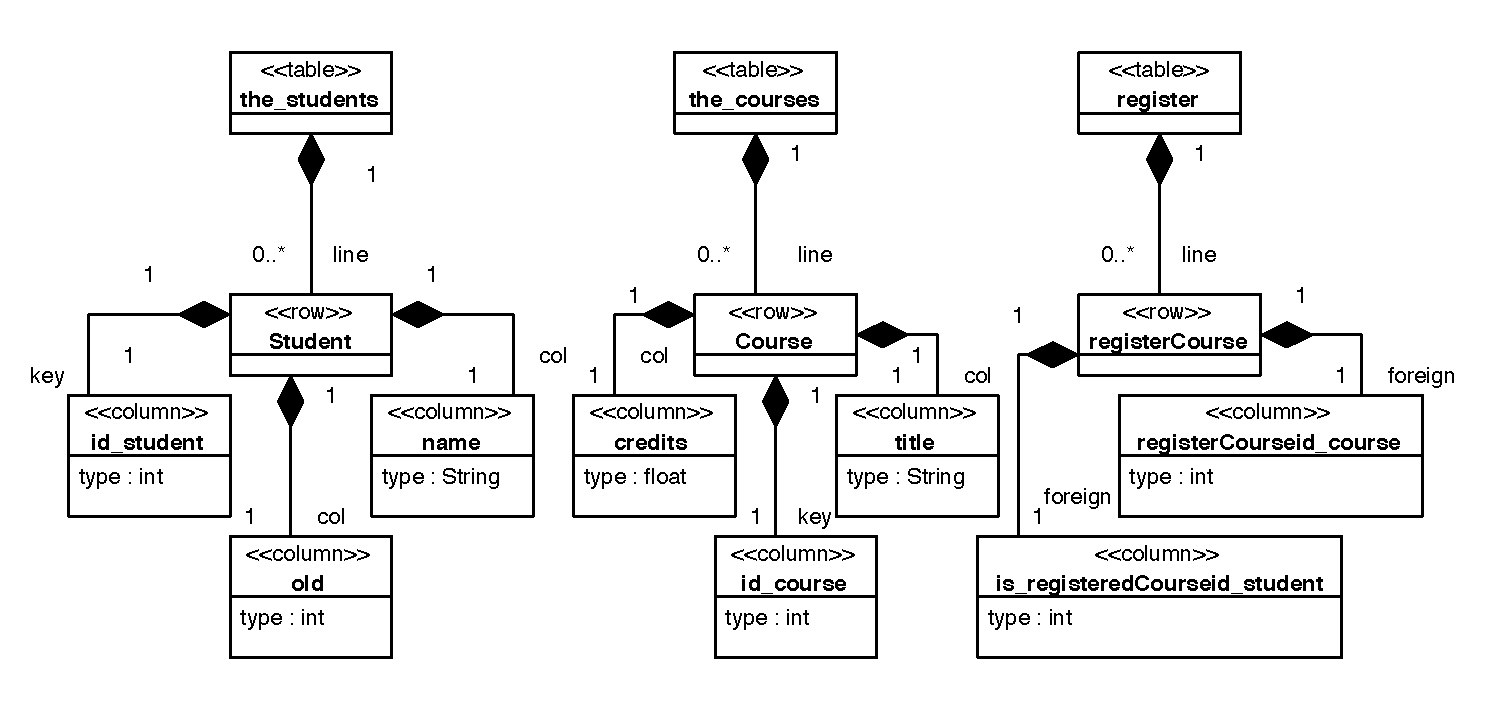
[home] [PNG] [PDF]
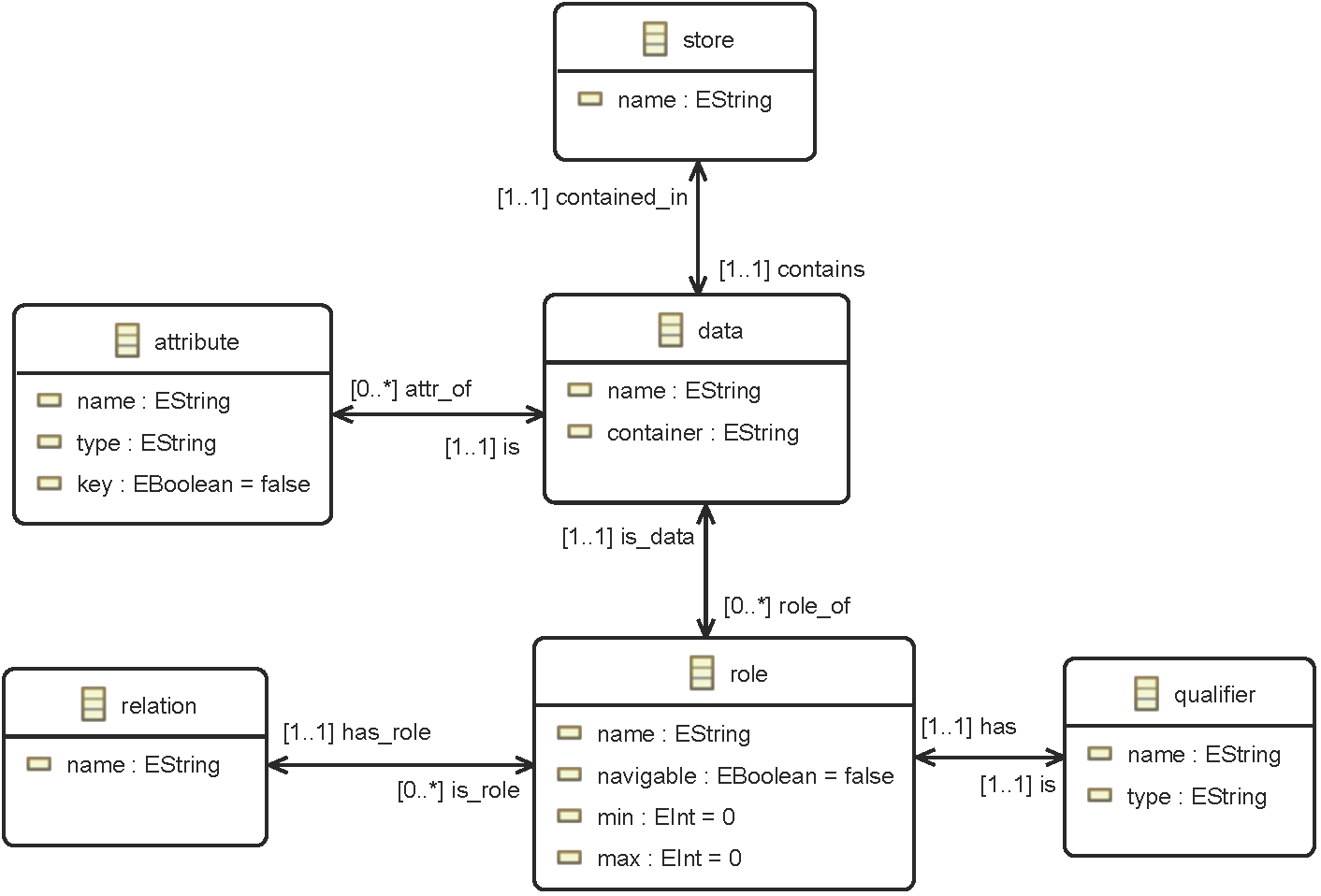
[home] [PNG] [PDF]
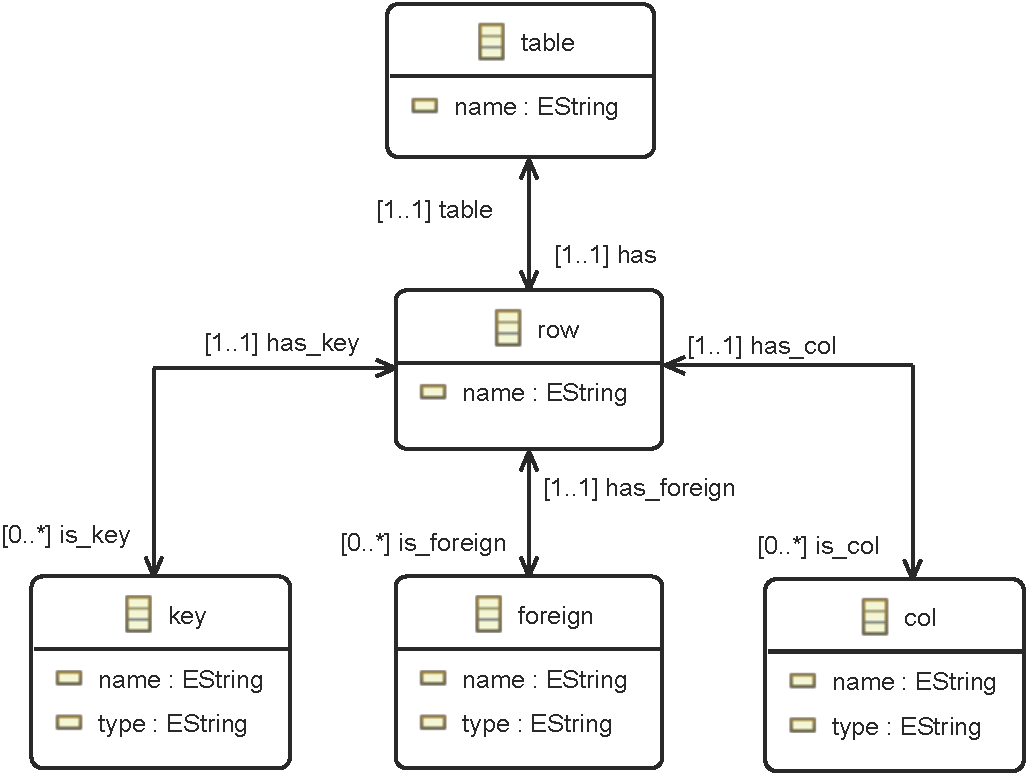
[home] [PNG] [PDF]
[home]
6.- Auxiliary
a) From ECORE to PTL: ecore2ptl.pl
b) From PTL to ECORE: ptl2ecore.pl
c) Loading
of
XMI files: loading.pl
d) Writing
of
XMI files: writing.pl
[home]
7.- PTL Eclipse plugin
To install the Eclipse plugin:
1. Install SWEProlog from http://www.swi-prolog.org.
2. Download Eclipse plugin: [PTL plugin]
3. Unzip the file and copy the content into the "features" and "plugin" folders.
4. Configure PTL interpreter in Eclipse preferences.
5. Create a "Transformation tool" project in Eclipse.
6. Create source code in folder "Transformers".
7. Run transformation, debugger, tracer and validator from Menu.
[home]
8.- Validation
a) PTL validation rules: ptl-validation.pl
b) OCL constraints: ocl-constraints-atl.txt
[home]
(c) Jesús Almendros and Luis Iribarne
University of Almeria, 2014
Department of Informatics
Almeria, Spain





